Kenya Transitions to Accrual Accounting: What Does it Mean?
Kenya’s move to accrual-based accounting is a significant step toward improving financial transparency and governance. This shift represents a modern approach to public financial management, where transactions are recorded when they occur rather than when cash is exchanged. The move offers Kenya several benefits, including better financial reporting and enhanced decision-making processes. However, as with any change, this transition comes with its share of challenges. Understanding both the benefits and the potential pitfalls is essential for a smooth adoption process.
What is Accrual-Based Accounting?
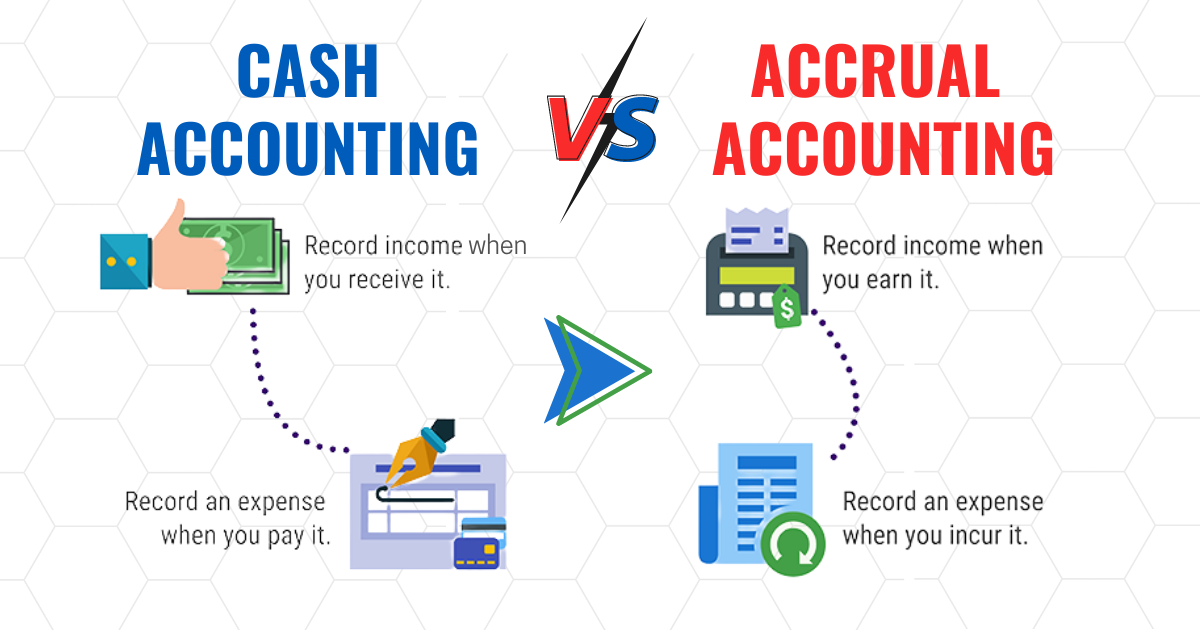
Accrual-based accounting is a method that records financial transactions when they are incurred rather than when payment is made. For instance, if a government project is completed in June, the expense will be recorded at that time, even if the payment is made in December. This differs from cash-based accounting, where transactions are only recorded when money changes hands.
The accrual system provides a clearer picture of a government’s financial health by capturing all liabilities and assets. It helps public institutions make better long-term decisions based on a full understanding of financial obligations and resources.
Why Is Kenya Shifting to Accrual-Based Accounting?
Kenya’s decision to adopt accrual accounting is driven by a desire to align with international standards. Many developed nations, including those in the European Union, have long used accrual accounting for their public sectors. Kenya’s shift will improve transparency, enabling clearer audits and giving a true picture of the country’s financial standing.
This change comes as part of Kenya’s larger strategy to improve governance and reduce corruption. Accurate financial records are a powerful tool in ensuring accountability. Accrual accounting can reveal hidden liabilities, such as unpaid debts, which cash accounting might overlook.
The Role of the Public Sector Accounting Standards Board
The Public Sector Accounting Standards Board (PSASB) has been instrumental in this transition. It has spearheaded efforts to train public sector employees and ensure that the shift is as smooth as possible. By setting guidelines and offering resources, the PSASB aims to ensure that Kenya’s public entities adhere to international accounting standards.
However, the road to full implementation of accrual accounting is complex. PSASB acknowledges that it will take several years for all public sector entities to fully embrace this new system.
The Benefits of Accrual-Based Accounting for Kenya
Accrual-based accounting offers several significant benefits for Kenya’s public sector:
- Improved Transparency
Accrual accounting provides a clearer view of the government’s financial position. By recording expenses and revenues as they occur, the system reveals the true financial health of public institutions. This enhanced transparency can help reduce corruption and foster greater accountability. - Better Financial Decision-Making
With a complete picture of liabilities and assets, government agencies can make more informed decisions. Accrual accounting shows the full financial impact of decisions, helping policymakers avoid hidden costs or overlooked debts. This long-term perspective is crucial for sustainable financial management. - Alignment with Global Standards
As more countries adopt accrual accounting, Kenya’s shift ensures that it remains competitive and aligned with global best practices. This alignment could make Kenya more attractive to international investors and financial institutions. - Enhanced Audit Processes
Auditors will have a more accurate financial snapshot, allowing for better oversight. The accrual method captures all transactions, reducing the likelihood of discrepancies or incomplete financial reports.
Challenges in Adopting Accrual-Based Accounting
While the benefits of accrual accounting are clear, the transition presents several challenges:
- Training and Capacity Building
Moving to an accrual-based system requires significant training for public sector employees. Many officials are familiar with cash accounting and will need to learn new skills. This training will take time and resources, and some government entities may face difficulties in adapting to the new system. - Initial Costs
Implementing accrual accounting will incur costs, including training, new software systems, and ongoing support. These expenses may strain public sector budgets, particularly in the short term. - Complexity in Implementation
Accrual accounting is more complex than cash accounting. Public entities will need to develop new processes to track transactions and obligations accurately. The increased complexity may lead to errors during the initial stages of implementation. - Resistance to Change
Change is often met with resistance, and some public sector employees may be reluctant to adopt the new system. Overcoming this resistance will require a strong commitment from leadership and clear communication about the benefits of accrual accounting.
Strategic Steps for a Successful Transition
Despite these challenges, Kenya can take several steps to ensure a smooth transition to accrual-based accounting:
- Comprehensive Training Programs
Training is crucial for the successful adoption of accrual accounting. The government should invest in comprehensive training programs to equip public sector employees with the necessary skills. This training should be ongoing, ensuring that employees stay updated on best practices. - Phased Implementation
A phased approach to implementation can reduce the risk of errors. Rather than attempting to switch the entire public sector at once, the government could focus on specific departments or regions. This would allow for lessons to be learned and improvements to be made before full adoption. - Investment in Technology
Accrual accounting requires modern financial systems to track transactions accurately. The government should invest in new accounting software and technology that can support the complexity of the accrual system. - Strong Leadership and Communication
Leadership plays a crucial role in the success of this transition. Government leaders must clearly communicate the benefits of accrual accounting and set a positive example by embracing the change. Regular updates and communication can help reduce resistance and keep the transition on track.
Conclusion: Embracing Change for a Stronger Future
Kenya’s transition to accrual-based accounting is a necessary step toward greater transparency and improved financial management. While challenges exist, the long-term benefits outweigh the short-term difficulties. With proper planning, training, and investment, Kenya can successfully navigate this shift and emerge as a leader in public sector financial management.
At MUIAA LTD, we offer tailored financial services that cater to any financial needs whether personal or business. Whether it’s project financing, investment advisory, or personal mortgage solutions, MUIAA is here to support your vision.